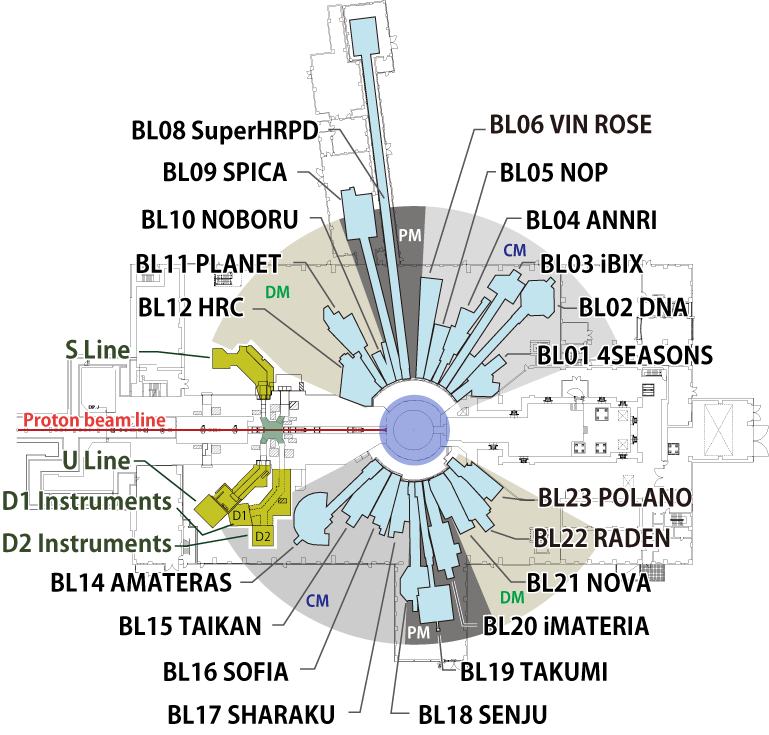
Neutron and Muon instruments
Neutron instruments
High-intensity pulsed neutron beams are generated 25 times per second in the neutron source of the MLF. As the wavelength of neutrons is inversely proportional to the speed, it can be determined by the time-of-flight (TOF) technique, the method to measure time between the neutron is generated and detected. At the neutron instruments in the MLF, by combining the high-intensified neutron beams generated from the neutron source and the sophisticated measurement technique using TOF, experiment that will contribute to the state-of-the-art science and technology is being conducted day and night.
There are 23 neutron beamlines in the MLF, and currently instruments are installed to 21 beamlines shown below.
Muon instruments
The muon source in the MLF MUSE (MUon Science Establishment) generates pions (π±) and “surface muons*” (μ+) as pulsed particle beams 25 times per second (pulse width: 0.1µs or shorter) by irradiating the graphite target with the 3-GeV proton beam to induce nuclear reaction with carbon. The pions are supplied to D line, and the surface muons are to U line and S line. At D line, energy-tunable positive/negative muons, which are produced by decay of pions in the superconducting solenoid beamline, are extracted as secondary beams and transported to instruments. The positive muons at U line is further reduced in energy to 103-4 eV before delivery to instruments. In the MLF currently four instruments are serving for the Inter-University-Research Program at D1, D2, U1, and S1 experimental areas. (The one at U1 is under commissioning).
*Positive muons with kinetic energy 4 MeV or lower that are obtained from decay of positive pions stopping near the surface of the graphite target.
In the MLF currently 4 instruments are installed to 3 beamlines. (One of them is in commissioning)
Layout of Instruments & Features